glaucoma
basics
The eye must have a certain dimensional stability to fulfill its functions, which is achieved by an internal pressure of about 14-20 mmHg. This intraocular pressure arises from the continuous formation of so-called aqueous liquid in the ciliary body behind the iris and a constant (necessary) outflow in the chamber angle (between the iris and the cornea).
Glaucoma refers to a range of eye diseases provoked by different causes where there is a mismatch between interocular pressure and "blood pressure", which means the failure of the circulation of the optic nerve. The result is a reduced blood flow and thus damage to the optic nerve.
Glaucoma is a chronic progressive eye disease and the second most common cause of blindness worldwide. The commonness of the disease increases with age and 2-4% of the people over 65 suffer from it.
Early detection gives the chance of early treatment and with it the avoidance of a gradual deterioration to prevent blindness. Nevertheless, there are approximately 1,000 new sight loss cases in Germany every year due to glaucoma.
Forms of glaucoma
- Aqueous fluid and eye pressure
The aqueous fluid formed in the ciliary body (behind the iris) surrounds the lens of the eye and the back surface of the cornea, thus ensuring the nutrition of these vascularized parts of the eye. For this purpose, a balance between production and outflow of aqueous fluid in the chamber angle (between cornea and iris) is required. - In narrow-angle glaucoma, the angle of the chamber is too narrow, it may become embarrassed, especially if the pupil is dilated. It can come to the glaucoma case.
- On the other hand, primary open-angle glaucoma can lead to an unnoticed imbalance of the pressure conditions, resulting in damage to the optic nerve fibers.
- Secondary glaucoma can occur as a result of various other diseases of the eye.
Diagnostics
- Organic examination
- Eye pressure measurement
- Functional tests
- Laser measurement of the eye
- Glaucoma screening diagnostics
Organic examination
Organic examination
The examination with the slit lamp takes place after the anamnesis, usually at the beginning of the examination. If need be The anterior segment of the eye will be assessed, possibly even the ocular fundus with a narrow pupil.
Eye pressure measurement
Eye pressure measurement
The measurement of intraocular pressure can be done by different methods, sitting or lying down. Nowadays, the so-called non-contact tonometers are often in use. They allow the internal pressure to be determined by the measurement of a defined air pulse and of corneal deformation. (see also research glaucoma)
Measurement of the dynamic intraocular pressure conditions with the Pascal Contour Tonometer:
The result of the examination provides decisive information on the perfusion of the eye, the most important protective factor against glaucoma. With this measurement, we can tell you even more precisely, if there is a risk of glaucoma and if a treatment is necessary.
Functional tests
Functional tests
Field of vision, perimetry
As a result of damage to the optic nerve, glaucoma causes (increasing) defects in the perception of the visual field outside central vision.
The task of "perimetry" is to use targeted examinations to examine different areas of the visual field and, as early as possible, to detect a decrease in the sensitivity of these areas or to control the course of visual field defects.
Methods
- Goldmann perimetry
- Automatic perimetry
- FDT ("Frequency doubling technology")
This visual field examination allows a particularly sensitive diagnosis for the early detection of glaucoma-related defects. It specifically tests the retinal sites that are affected early in glaucoma.
Laser measurement of the eye
Laser measurement of the eye
As a precaution, we offer you a special program, which we would like to introduce to you. These benefits are not included in the scope of benefits of the statutory health insurance.
Non-contact measurement of corneal thickness
The measurement of "normal" eye pressure (10-20 mmHg) does not exclude the diagnosis of glaucoma. To note is the corneal thickness when measuring intraocular pressure. A cornea that is thicker than the "norm" gives the fasle information of a higher intraocular pressure. Too thin a cornea covers up an incresased pressure.
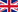
| Surveying the optic nerve head with the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph (HRT III) For further improvement in glaucoma diagnosis, we offer the examination of the optic nerve with a three-dimensional measurement of the optic nerve head with a laser scanner, the HRT III. |
healthy optic nerve |
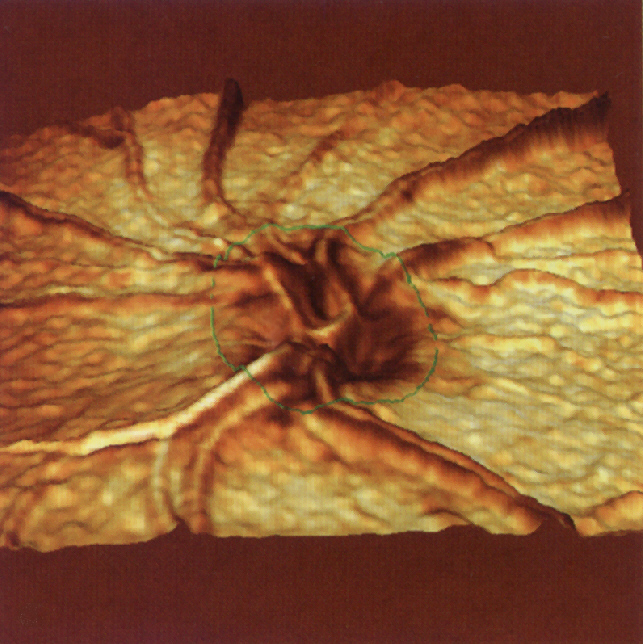
| Thus, a diagnosis in the early stages and a later follow-up for glaucoma are possible. During the process a comparison of the many precisely determined values of the optic nerve surface is possible and thus the detection of even the smallest changes. |
Optic nerve changed by glaucoma |
| The HRT III examination is the only objective assessment of the optic nerve and thus provides an independent follow-up over the years. |
Treatment
Glaucoma can be treated with eye drops, laser surgery or surgery. The goal is to lower the intraocular pressure and thereby reduce the risk of visual damage and blindness.
The term glaucoma refers to various eye diseases in which the optic nerve is damaged. As a result, the field of view always has larger gaps. In advanced stages, visual acuity also decreases. A common cause is usually too high intraocular pressure.
Reducing high intraocular pressure can help delay or halt the gradual vision loss. Glaucoma can not be cured, as already incurred damage can not be reversed. That's why we always recommend glaucoma care.
Medicinal therapy
Medicinal therapy
In the therapy of glaucoma, various substances are available, which are usually administered as eye drops today.
- Beta blockers: They reduce the production of aqueous fluid and are often prescribed as the first remedy.
- Cholinergics: they increase the outflow of aqueous fluid. Also cholinergics are proven drugs for the treatment of Glaucoma.
- Prostaglandins: They also increase the outflow of aqueous fluid and, like beta-blockers, are often prescribed as the first remedy.
- Alpha agonists: They reduce the production of aqueous fluid while increasing its efflux.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: they reduce the production of aqueous fluid.
The choosing of an appropriate remedy depends on various factors. We are happy to advise you.
Side effects
The eye drops can have different side effects. Any remedy can irritate the eye and cause, for example, itching and redness. Some agents - some beta blockers - can stress the cardiovascular system and breathing. To reduce the likelihood of side effects, it is recommended to close the eyes for three minutes after dripping. You can also slightly close the inner corner of the eye with your finger. Both should ensure that the drops works in the eye and do not flow into the nasopharynx, where they are absorbed into the body via the mucous membrane.
Operations
Operations
If adequate lowering of the intraocular pressure by drugs (e.g., drops, tablets) is not successful or possible, we recommend glaucoma surgery. Its purpose is to improve the outflow of aqueous fluid or to reduce the formation of aqueous fluid.
The procedure is performed either in local anesthesia by drip anesthesia or injection of an anesthetic under the conjunctiva or next to the eyeball or in general anesthesia. Each patient will be informed separately about the proposed procedure, its effects and possible side effects / risks as well as its advantages and disadvantages.
There are various surgical procedures, the essentials of which we will list below. The glaucoma operations are ophthalmological standard procedures. They are performed under the surgical microscope, some using laser technology. We will explain the advantages and disadvantages of the various procedures in a personal discussion.
The following information is taken from the information sheet "Operation des Grünen Stars" (Editor: Prof. K. Ulsenheimer (Medical Law), Founding: Prof. W. Weißauer, Specialist: Prof. T. Kohnen, Authors: Prof. M. Diestelhorst, Prof. T. Kohnen, Diomed in Thieme Compliance GmbH):
- "Iridectomy: a small opening gets surgically created In the periphery of the iris by a precision knife, , which improves the outflow of the aqueous fluid over the chamber angle.The iridectomy is used mainly with narrow angle (narrow-angle glaucoma) and with an increasment of acute intraocular pressure ("glaucoma case")
- Iridotomy: a small opening gets created In the periphery of the iris, this time form the outside by laser beams, which improves the outflow of aqueousfluid through the chamber angle. Unlike surgical iridectomy, the eye does not need to be opened. The iridotomy is mainly used in narrow angle of the the eye and in case of an increasment of acute intraocular pressure (glaucoma case).
- Filtration Surgery/Trabeculectomy: A new drainage path is created under the conjunctiva through a very small opening in the dermis and an iris window (iridectomy) is created in this area. This allows the aqueous fluid to be drained more easily from the eye to the eye socket.
- Goniotomy, Trabeculotomy, Goniocurettage: e.g. In congenital glaucoma, a fine needle-like knife or similar instrument / trabectome is used to cut tissue / membranes in front of the trabecular meshwork to improve drainage of the eye water from the anterior segment.
- Viscocanalostomy/-canaloplasty: Similar to chamber angle surgery (# 4), a gel-like substance / plastic filament is injected / clamped into the drainage channel to improve the outflow of aqueous fluid.
- Cyclo-cryo-photocoagulation: A part of the ciliary body that forms the aqueous fluid is desquamated by a cold stick (cyclocryocoagulation) or by laser energy (cyclophotoagulation). As a result, less eye water is formed in the subsequent period. This method is often performed on secondary glaucoma, e.g. as a result of existing eye inflammation, thrombosis in the eye or vascular changes (diabetes) arise.
- Selective laser trabeculoplasty laser surgery (SLT): After anesthesia of the cornea and the placement of a contact lens, the chamber angle in selected sections is treated with low-dose laser light. This procedure is suitable for low increasement in intraocular pressure "(end of quote) and is often recommended even before a drip therapy. SSLT laser therapy uses very short light pulses with low energy and aims only at the specific melanin or pigment cells in the eye. These cells are then renewed via a regenerative, self-healing process of the body; in this natural way the aqueous drainage is restored. The treatment can be performed on an outpatient basis and usually lasts no more than five minutes. Due to the green laser light pulses, which are very short (0.000000003 seconds) and extremely low dose, the laser energy is only selectively transferred to the pigment cells in the eye. Through a regenerative, self-healing process of the body, these cells are renewed. The surrounding tissue and the rest of the eye remain completely untouched and undamaged. The drainage is no longer blocked, consequently the aqueous fluid can flow freely again and the intraocular pressure drops. Compared to other laser therapies, SLT is a gentle, non-invasive, tissue-sparing treatment that can be safely repeated. The SLT treatment is particularly useful when/with:
● Open-angle glaucoma, pseudoexfoliation glaucoma or pigment glaucoma
● you can not tolerate glaucoma drops or have difficulty dropping.
● you already have glaucoma drops and you want to combine the SLT.
● it is difficult for you to take regular check-ups and treatments.
●you have had an ALT (Argon Laser Trabeculoplasty) treatment and your eye pressure has risen again.
What happens if SLT cannot lower eye pressure?
SLT reduces eye pressure by up to 30% and affects 75 to 85% of treated patients. If the SLT does not work for you, your doctor will continue to use traditional drug therapy and specialized surgery.
Furthermore, the following two options are cited from the above named work: - "Implants: The aqueous fluid is discharged via a small implant (plastic tube) from the eye chamber into the eye socket and so the intraocular pressure lowered.
- Combination of Filtration Operation (#3, #4) and Cataract Operations: Modern surgical techniques allow cataract and glaucoma to operate simultaneously. Here, the clouded lens (cataract) is liquefied via a corneal incision by means of ultrasonic energy (phacoemulsification), aspirated and a new plastic lens is used to improve vision. If this procedure is suitable for your eyes, you will be informed separately. "(End of quote)
Research
The measurement of intraocular pressure is still one of the most important diagnostic tests. However, all common methods have inadequacies. That's why we designed different measurement options based on electronic principles.
1983-1990 concept and patent applications for electronic applanation tonometry