Cornea
Diagnostics
Slit lamp
Slit lamp
The slit lamp (slit lamp microscope) is one of the most important ophthalmic examination devices. Using a microscope, the examiner can look at the eye with varying magnification
- through different types of exposure (diffuse, direct, indirect, focal, regressive, etc.)
- with different light gap widths
- from the front to the back of the eye, possibly with additional optics.
Corneal topography
Corneal topography
In this procedure, originally only the surface of the cornea was measured by the projection of concentric rings of light, later also luminous dots or slit images. However, modern devices also allow the measurement of the corneal surface, the corneal thickness of one certain area, the shape, the refractive power and radii, the astigmatism. In addition, there is information about the anterior chamber depth and shape and much more.
CornealOCT
Corneal OCT
The optical coherence tomography (OCT) allows (in addition to the known diagnosis of the retina) investigation of the cornea, anterior chamber and partially the dermis. In particular, in the non-contact examination, the layers of the cornea can be precisely represented in the sectional image.
Treatment
PTK
PTK - Phototherapeutic keratectomy
Main indications:
- Recurrent corneal erosions
- Superficial corneal scars
Laser beams remove superficial layers of tissue after removal of the epithelium.
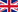
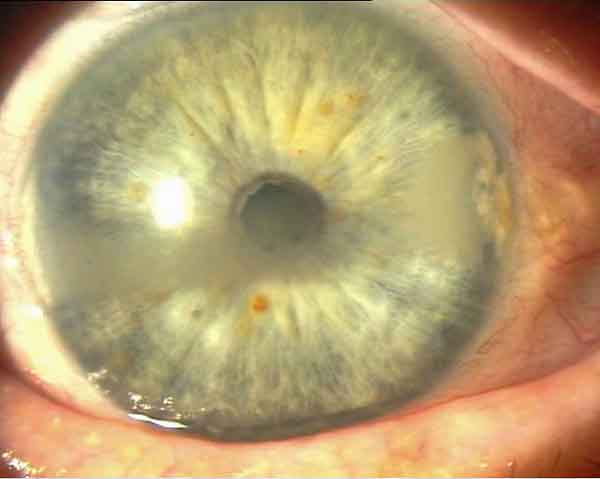 Linear corneal dystrophy (before PTK)
Linear corneal dystrophy (before PTK)
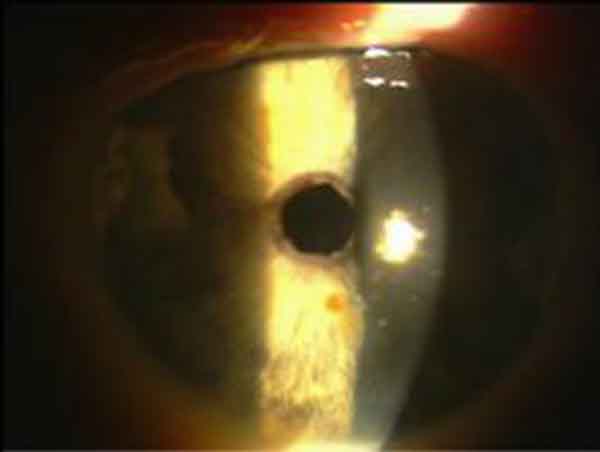 Corneal erosion (after PTK)
Corneal erosion (after PTK)
How is the treatment carried out?
The PTK is performed under local anaesthesia by eye drops. Syringes are not required. In addition, the patient receives a mild tranquilizer. First, a large area of the corneal epithelium is mechanically removed. With the laser, the corneal change is now "grinded" without contact under a surgical microscope within a few seconds (see Fig. 1). After the laser treatment, a therapeutic contact lens is applied as a "transparent bandage" for about a week on the eye. The patient receives additional eye drops.
Healing process
The surgical wound heals under the contact lens within a few days. During this time, sometimes partly more severe pain occurs, despite the lens. The vision is blurred. These complaints resolve after a few days.
Thereafter, a second, slow healing phase sets in, which can take up to six months or more. In the first few months, slight corneal opacities may occur; the eye is particularly sensitive to light and glare in this time. The driving of a motor vehicle (especially in the dark) and / or the professional practice can be made difficult or impossible. Treatment with eye drops, containing cortisone may be required.
This operation has been a statutory health insurance benefit since 1 October 2007. Until then, affected patients had to bear the operating costs themselves. Now the patient incurs no costs, only for a necessary additional diagnostics. An application to the health insurance is not necessary.
We carry out the PTK ourselves since 2001 with great success. Patients with recurrent erosion are usually symptom-free afterwards. This leaves them with another tale of woe including pain, sick leave, medication, etc. spared. Eyes with central superficial corneal opacities usually show an increase in visual acuity following tissue abrasion.
Our patients are examined for any complaints that may arise for a laser treatment worth considering and appointments are made for the operation. Patients from other ophthalmic practices need a referral from their ophthalmologist. An appointment can be made promptly.
If you have further questions, please contact our team or the clinic.
CXL-Crosslinking
CXL = UV-riboflavin crosslinking (=Corneal Cross Linking)
Cross linking can be compared to a net that strands and thus becomes more stable. The combination of riboflavin eye drops (Vitamin B2) and UV rays provides the corneal fibres with a cross-link, making the corneal shape more stable, and thus, according to the current state of knowledge, no further protrusion occurs.
Crosslinking of tissues is not a new technology in medicine. In fact it has been used in dentistry, orthopaedics, ENT and cardiac surgery for many years. It has also been successfully performed on the eye for more than 7 years. The procedure is now used in everyday clinical practice, but is not a specifically approved procedure.
The treatment
The treatment is performed under sterile conditions with local anaesthesia and takes about 60 minutes in total. First, a lid holder is used to keep your eye open during treatment. In order to allow the riboflavin eye drops to enter the cornea, the top layer of the cornea (epithelium) is removed in the first step. Subsequently, the cornea is soaked for 30 minutes with the eye drops, then irradiated for 30 minutes with UV light while further dripping. In order for the epithelium to heal again, the patient receives a "bandage" contact lens at the end of treatment, which remains on the cornea for approximately 4 to 5 days.
Treatment aim
The aim of the Crosslinking treatment is to stabilize the cornea and stop the progressive protrusion. The disease cannot be cured, but the existing condition is "frozen". If another operation has to be performed later, this is possible at any time.
We carry out this treatment at the Potsdam Eye Clinic since 2008.
Varia
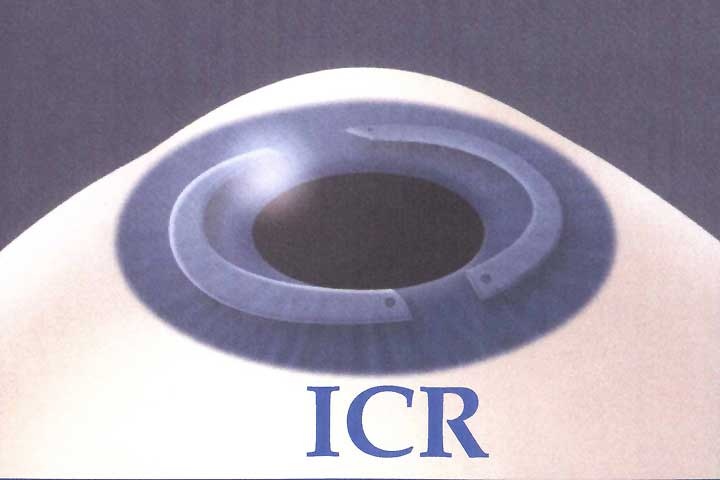
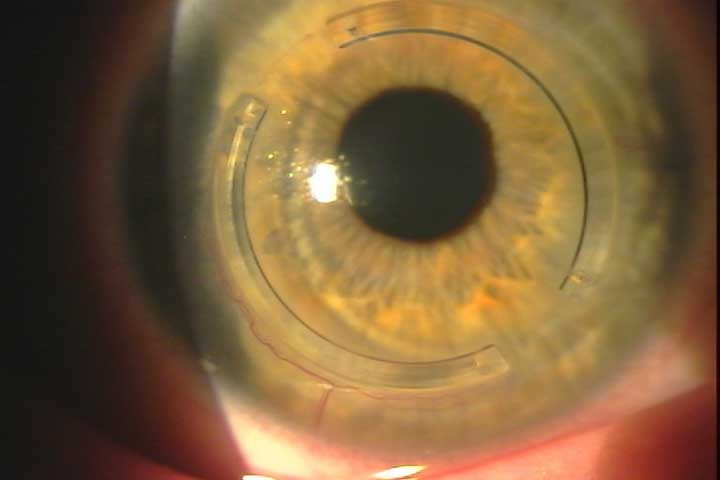
Intacs - intracorneal ring segments
The intacs were originally used for the refractive correction of myopia by about -1 to -4 dioptres. Due to the resulting change in the shape of the cornea, there was an increase in aberrations and the emergence of unwanted corneal curvatures and other complications.
Today, the segments are mainly implanted to stabilize the cornea in the case of keratoconus. We prefer surgical preparation of the ring tunnel with the intralase femtosecond laser.